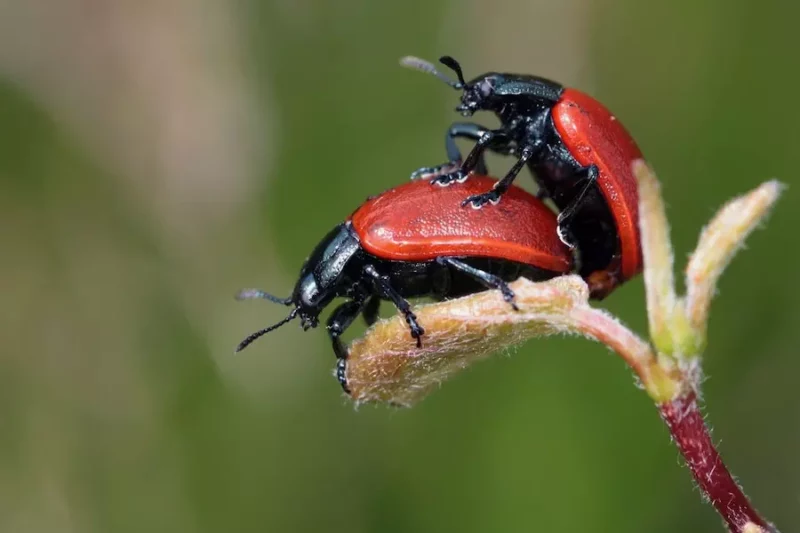
Reproduction is a fundamental aspect of life on Earth, and it is responsible for the incredible diversity of living things that exist today. From microscopic bacteria to complex mammals, all living things share a common goal – to produce offspring that can carry on their genetic legacy. The process of reproduction has fascinated scientists and curious minds for centuries, and it continues to be a subject of extensive research and exploration.
In this guide, we’ll peek into the basics of reproduction and explore the various ways that living things multiply. We will examine the different reproductive strategies of plants and animals, including sexual and asexual reproduction. Additionally, we will take a closer look at the intricate processes involved in fertilization and embryonic development, and discuss the importance of genetic diversity in ensuring the survival of species. Whether you are a student of biology, a science enthusiast, or simply curious about the wonders of life on Earth, this blog post is sure to be both informative and engaging.
Curious about how reproduction works? Click this link: reproductive system for kids.
1. Overview of Reproduction
Reproduction is the biological process by which new individuals of the same species are produced, either sexually or asexually. Sexual reproduction involves fertilization of gametes produced by male and female organisms, resulting in the creation of offspring with unique genetic traits. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, is the process by which an individual organism reproduces without the involvement of gametes, resulting in genetically identical offspring. Reproduction is essential for the survival and adaptation of species in changing environments, and understanding the mechanisms by which living things multiply is a critical aspect of the study of biology.
2. Sexual Reproduction And Its Components
Sexual reproduction is a fundamental biological process through which new life is created. It involves the fusion of gametes, or sex cells, from two individuals to produce a unique offspring that inherits traits from both parents. The components of sexual reproduction include the matured gametes, which are haploid cells meant to combine and produce a new diploid zygote. In animals, gametes are produced through the process of meiosis, which halves the chromosome number in half. The male gamete is usually small and mobile, known as a sperm cell, while the female gamete is generally larger and immobile, known as an egg cell. The fusion of a sperm and egg cell is called fertilization, resulting in the formation of a zygote that undergoes rapid cell division to form an embryo. Sexual reproduction is a complex, but essential process that ensures genetic diversity in populations, allowing offspring to inherit a variety of traits from their parents that enhance their ability to survive and adapt to changing environments.
3. Asexual Reproduction And Its Components
Asexual reproduction is a biological process by which offspring are produced without the involvement of gametes or sex cells. This is in contrast to sexual reproduction, which requires the fusion of a male and female gamete to form a zygote. Asexual reproduction is common in many single-celled organisms, as well as a number of multicellular organisms, such as plants and fungi. There are three main types of asexual reproduction: binary fission, budding, and fragmentation. Binary fission is characterized by the splitting of a single cell into two daughter cells, both of which are identical to the parent cell. Budding refers to the splitting off of a smaller, self-contained portion of the parent organism that will grow and develop into a new individual. Fragmentation, on the other hand, involves the breaking off of a piece of the parent organism, which will then develop into an entirely new organism.
4. Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which living organisms multiply and create new cells. This process occurs through two main mechanisms: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is the form of cell division used by most organisms to create new cells for growth and repair. During mitosis, a cell duplicates its DNA and divides into two identical daughter cells. Meiosis, on the other hand, is the process by which sexually reproducing organisms create haploid cells, which are cells with half the normal number of chromosomes. These haploid cells are ultimately used to create genetically diverse offspring. Cell division is essential to the reproduction and overall survival of living organisms, as it enables growth, repair, and reproductive processes.
5. Types of Reproduction
In the world of biology, the concept of reproduction is fundamental to the survival and ongoing evolution of living things. From single-celled organisms to complex multicellular organisms, the ability to reproduce is central to the continuation of individual species. There are different types of reproduction that exist in organisms, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages. The five types of reproduction commonly recognized in biology are asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction, hermaphroditism, parthenogenesis, and cloning. Understanding the different types of reproduction and how they work can provide invaluable insights into the biology and evolution of living organisms. In this document, we will explore each of these forms of reproduction in detail, highlighting the key characteristics and biological mechanisms that underpin them.
6. Role Of Reproduction In Ecosystems
The role of reproduction in ecosystems is essential to the survival of living species. It serves as a means of ensuring genetic diversity within populations, thus reducing the risk of inbreeding and increasing the species’ resilience to environmental stresses. Moreover, reproduction cycles aid in maintaining the balance among organism populations in terms of predator-prey relationships and resource allocation. Reproduction also allows for the transfer of traits that provide advantages such as resistance to diseases or adaptation to changing environments. Understanding the complex mechanisms of reproduction is critical for managing biological communities and identifying potential challenges to maintaining ecosystem homeostasis. In our exploration of the basics of reproduction, we will delve into the intricacies of this vital process and its impacts on ecosystems.
7. Summary And Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of reproduction is fascinating, complex, and crucial to the continuation of life on Earth. We have explored the various types of asexual and sexual reproduction and the mechanisms by which organisms multiply. We have also examined the advantages and disadvantages of each type of reproduction and how it affects the survival and diversity of species. By understanding the basics of reproduction, we can appreciate the intricacy and diversity of life around us. Whether it is through binary fission, budding, fragmentation, or gamete formation, the ability of living things to multiply and pass on their traits is truly remarkable. It is essential to note that reproduction is not only limited to individuals but it is also a fundamental aspect of the evolution of species. The perpetuation of genetic information is essential to the survival of species and to the development of new ones. By studying the reproductive strategies of different organisms, we can gain insights into their biology and behavior. Overall, it is clear that the study of reproduction is a vast and fascinating field that plays a critical role in understanding the complexity of living things.